Chapter No: 2 “SUPPORT AND MOVEMENT
No: of Items: 94
Q:1: Movement takes place at
(A) Cellular level (B) Organ level
(C) Organism level (D) All A, B and C
Q:2: The whole body of Bryophyta is made up of
(A) Collenchyma cells (B) Sclerenchyma cells
(C) Parenchyma cells (D) Aerenchyma cells
Q:3: Collenchyma can be distinguished from parenchyma by
(A) Being dead cells (B) Without large vacuole
(C) Increased thickness of their cell walls (D) All A, B and C
Q:4: A tissue whose function is support and it performs that function while it is dead is _____________________.
(A) Collenchyma (B) Parenchyma
(C) Sclerenchyma (D) A and B
Q:5: In angiosperms the tissue that produces secondary xylem and secondary phloem is
(A) Protoderm (B) Ground meristem
(C) Intercalary meristem (D) Vascular cambium
Q:6: The unspecialized packing tissue found in epidermis, cortex and pith is
(A) Parenchyma (B) Collenchyma
(C) Sclerenchyma (D) Cork cambium
Q:7: Xylem vessels have walls impregnated with
(A) Cutin (B) Chitin
(C) Keratin (D) Lignin
Q:8: The ___________ covers the plant but is replaced by ________________.
(A) Cuticle, epidermis (B) Endodermis, Epidermis
(C) Epidermis, cork (D) All A, B and C
Q:9: Secondary growth in plants begins with the formation of
(A) Vascular cambium only (B) Cork cambium only
(C) Vascular and cork cambium (D) Inter-calary meristems
Q:10: Cork is waterproof because its cell walls are impregnated with
(A) Chitin (B) Suberin
(C) Keratin (D) Pillin
Q:11: It is the xylem in the center of the tree that has stopped conducting water and minerals and is storing waste products from the plant.
(A) Sap wood (B) Heart wood
(C) Peripheral wood (D) Both B and C
Q:12: It is the portion of the xylem that is conducting water and minerals and hasn't started storing waste products.
(A) Sap wood (B) Heart wood
(C) Central wood (D) Both A and C
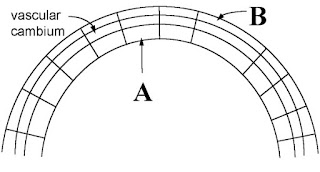
Q:13: Select the correct option for Label "A" and "B" in the following diagram?
(A) "A" New Phloem, "B" New Xylem (B) "A" New Cork, "B" New Cortex
(C) "A" New Cork, "B" New Phelloderm (D) "A" New Xylem, "B" New Phloem
(C) "A" New Cork, "B" New Phelloderm (D) "A" New Xylem, "B" New Phloem
Q:14: Lenticels are necessary for
(A) Photosynthesis (B) Gaseous exchange
(C) Water absorption (D) All options are correct
Q:15: Movement of Railway creeper around any rope is an example of
(A) Nutation (B) Turgor movement
(C) Tropic movement (D) Seismonastic movement
Q:16: ______________ is directional movement response that occur in response to a directional stimulus.
(A) Nutation (B) Tropism
(C) Both A and B (D) Turgor movement
Q:17: Tropic movement in response to touch is known as
(A) Geotropism (B) Aerotropism
(C) Thigmotropism (D) Both B and C
Q:18: The growth of the pollen tube is always towards the ovules, it is due to
(A) Geotropism (B) Thigmotropism
(C) Phototropism (D) Chemotropism
Q:19: The movement of a plant in response to a touch or contact is
(A) Nyctinastic (B) Thermonastic
(C) Haptonatic (D) Hyponastic
Q:20: The flowers of Oxalis and Portulaca open in the day and close at night. It is
(A) Nyctinastic movement (B) Thermonastic movement
(C) Haptonatic movement (D) Thigmonastic movement
Q:21: Exoskeleton in Diatoms is made up of
(A) Protein (B) CaCO3
(C) Silica (D) Chitin
Q:22: Molluscs have an exoskeleton in the form of
(A) Proteinteous shell (B) Siliceous shell
(C) Calcareous shell (D) Chitineous shell
Q:23: The periodic shedding of exoskeleton in arthropods is known as
(A) Moulting (B) Ecdysis
(C) Both A and B (D) Stridulation
Q:24: Human endoskeleton is about _____________ of the total body weight.
(A) 80% (B) 70%
(C) 40% (D) 18%
Q:25: The tooth bearing bone of lower jaw is
(A) Atlas (B) Innominate
(C) Incus (D) Dentary
Q:26: An adult human endoskeleton consists of
(A) 363 bones (B) 639 bones
(C) 206 bones (D) Number varies by the individual
Q:27: The lower two pairs of ribs are
(A) True ribs (B) False ribs
(C) Floating ribs (D) All A, B and C
Q:28: Total number of ribs in your axial skeleton is
(A) 12 (B) 24
(C) 33 (D) 26
Q:29: The original number of vertebrae in human vertebral column is
(A) 12 (B) 24
(C) 33 (D) 26
Q:30: The visible number of vertebrae in human vertebral column is
(A) 12 (B) 24
(C) 33 (D) 26
Q:31: Humerus forms a ball and socket joint with
(A) Clavicle (B) Sternum
(C) Innominate (D) Scapula
Q:32: The bones of lower arm are
(A) Tibia and fibula (B) Radius and ulna
(C) Carpals and metacarpals (D) Phalanges
Q:33: Which one of these makes bones hard?
(A) Carbohydrates (B) Minerals
(C) Proteins (D) Fats
Q:34: Which of the following is not part of the axial skeleton
(A) Sternum (B) Vertebrae
(C) Femur (D) Skull
Q:35: In human’s back bone the Caudal vertebrae are reduced to 4 in number and are fused to form the
(A) Sacrum (B) Innominatum
(C) Coccyx (D) Ischium
Q:36: Bones are joined to each other at joints by
(A) Tendons (B) Ligaments
(C) Hyaline cartilage (D) Both A and B
Q:37: Muscles are attached to bones by
(A) Tendons (B) Ligaments
(C) Synovial membrane (D) Both A and C
Q:38: It is a _____________________ joint that allows the skull to rotate on our spine.
(A) Hinge joint (B) Fibrous joint
(C) Sliding joint (D) Pivotal joint
Q:39: Between each vertebrae are pads of __________________ called intervertebral disks which absorb shock and assist in limited movement of disks.
(A) Collagen fibers (B) Osteonectin protein
(C) Cartilage (D) All A, B and C
Q:40: The normal backbone is not straight, but has four curves. The curve in the region of the neck is composed of seven vertebrae and is known as the
(A) Lumbar region (B) Sacral region
(C) Coccygeal region (D) Cervical region
Q:41: The 12 vertebrae in the second curve of vertebral column are known as
(A) Cervical vertebrae (B) Thoracic vertebrae
(C) Lumbar vertebrae (D) Sacral vertebrae
Q:42: The shoulder girdle consists of two bones
(A) Humerus and Scapula (B) Humerus and Ulna
(C) Clavicle and Scapula (D) Ilium and Ischium
Q:43: The pelvic girdle is composed of three pairs of fused bones
(A) Ilium, Ischium and frontal (B) Clavicle, Scapula and pubis
(C) Malleus, Incus and stapes (D) Ilium, Ischium and pubis
Q:44: Select the correct option for label "16" in the following diagram.
(A) Patella (B) Fibula
(C) Tibia (D) Radius
Q:45: The bones of the wrist are called
(A) Carpals (B) Metacarpals
(C) Tarsals (D) Metatarsals
Q:46: The joint found between the flat bones of the skull is classified as
(A) Immovable (B) Movable
(C) Slightly movable (D) None of these
Q:47: These cells are located in bone tissue
(A) Chondroblasts (B) Osteocytes
(C) Fibroblasts (D) Chondrocytes
Q:48: Chondroblasts produce
(A) Basement membranes (B) Bone matrix
(C) Cartilage matrix (D) Endothelium
Q:49: Gliding joints are present between
(A) Carpals and tarsals (B) Humerus and ulna
(C) Femur and innominate (D) Vertebrae
Q:50: Which type of joint is the most mobile?
(A) Pivot joint (B) Gliding joint
(C) Ball and socket joint (D) Fibrous joint
Q:51: The main protein in the matrix of cartilage is
(A) Collagen (B) Osteonectin
(C) Keratin (D) Actin
Q:52: The Jointed surfaces of bones are covered with
(A) Hyaline cartilage (B) Compact cartilage
(C) Articular cartilage (D) Both A end C
Q:53: The process of bone formation is called
(A) Ossification (B) Chondrification
(C) Ossi-chondrification (D) Both A and C
Q:54: Hinge joint is present between
(A) Humerus and radio-ulna (B) Femur and pectoral girdle
(C) Femur and acetabulum (D) Humerus and pectoral girdle
Q:55: The total number of bones in your right arm is
(A) 30 (B) 32
(C) 35 (D) 60
Q:56: Which bone in Man is concerned with locomotion
(A) Ulna (B) Femur
(C) Humerus (D) All of these
Q:57: It is spinal degeneration and deformity of the joints of two or more vertebrae that commonly occurs with aging.
(A) Sciatica (B) Osteoporosis
(C) Spondylosis (D) Both B and C
Q:58: In which skeletal deformity pain is felt in the lower back, buttock, and/or various parts of the leg and foot.
(A) Sciatica (B) Osteoporosis
(C) Arthritis (D) All of these
Q:59: Which of the following groupings is incorrect?
(A) Skeletal, striated, voluntary (B) Smooth, unstriated, involuntary
(C) Cardiac, striated, voluntary (D) Cardiac, striated, involuntary
Q:60: The muscle tissue that can be consciously controlled is
(A) Smooth (B) Skeletal
(C) Intercalated (D) Cardiac
Q:61: Which condition is shown in following diagram?

(A) Cleft Lip (B) Cleft Palate
(C) Incomplete cleft palate (D) Unilateral complete lip and palate
(C) Incomplete cleft palate (D) Unilateral complete lip and palate
Q:62: Skeletal muscle is described by all of the following EXCEPT
(A) Striated (B) Voluntary
(C) Multinucleate (D) Autorhythmic
Q:63: The walls of digestive tract and blood vessels contain this muscle tissue
(A) Striated (B) Skeletal
(C) Cardiac (D) Smooth
Q:64: The smallest contractile unit of skeletal muscle is a
(A) Sarcomere (B) Motor unit
(C) Synapse (D) Thin filament
Q:65: The major regulatory proteins in muscle tissue are
(A) Myosin and tropomyocin (B) Myosin and actin
(C) Actin and troponin (D) Troponin and tropomyocin
Q:66: Muscles that straighten two bones at joints are called extensors. What is the name for muscles that cause two bones to bend at joints?
(A) Protractors (B) Flexors
(C) Adductors (D) Abductors
Q:67: Which of the following is the best description of cardiac muscle?
(A) Non-striated – Involuntary (B) Non-striated – Voluntary
(C) Striated – Involuntary (D) Striated – Voluntary
Q:68: The loss of bone density is called_____________ and can cause bones to become light, brittle, and easily broken.
(A) Spondylosis (B) Arthritis
(C) Sciatica (D) Osteoporosis
Q:69: Inflammation of the joint is known as
(A) Bursitis (B) Arthritis
(C) Both A and B (D) Nephritis
Q:70: A ______________ is single somatic motor neuron and the group of muscle fibers innervated by it.
(A) Somatic unit (B) Motor unit
(C) Associative unit (D) None of these
Q:71: The bicep and tricep muscles are found in
(A) Shank (B) Shoulder
(C) Upper arm (D) Lower jaw
Q:72: During muscular contraction
(A) Actin slide past myosin (B) ATP supplies energy
(C) calcium ions (Ca++) are involved (D) All of these
Q:73: A skeletal muscle cell
(A) has light and dark bands (B) has only one nucleus
(C) is under involuntary control (D) None of the above are true
Q:74: The proteins at the junctions between sarcomeres form the
(A) H zone (B) M line
(C) Z line (D) A band
Q:75: Thick myofilaments are composed of several hundred molecules of a fibrous protein known as
(A) Actin (B) Myosin
(C) Troponin (D) Tropomyocin
Q:76: Thin myofilaments are composed of two helically interwound, linear polymers of a globular protein known as
(A) Actin (B) Myosin
(C) Troponin (D) Tropomyocin
Q:77: A disk-like protein which is centrally located in sarcomeres is
(A) H line (B) M line
(C) Z line (D) I line
Q:78: Within a sarcomere _____________ thin filaments are arrayed around each thick filament.
(A) 4 (B) 6
(C) 2 (D) 8
Q:79: Changes in sarcomere length are caused by the thin filaments being pulled along the thick filaments in the direction of the
(A) H zone (B) M line
(C) Z line (D) I band
Q:80: Tetany characteristically is considered to result from a severe degree of
(A) Hyperglycemia (B) Hypercalcaemia
(C) Hypocalcaemia (D) Hypoglycemia
Q:81: The contraction of muscles depends upon
(A) Nerve impulse (B) Energy
(C) Calcium ions (D) All of these
Q:82: Human eye muscle contracts in
(A) 0.01 seconds (B) 0.05 seconds
(C) 0.08 seconds (D) All options are incorrect
Q:83: Bicep muscles are
(A) Flexor muscles (B) Extensor muscles
(C) Adductor muscles (D) Abductor muscles
Q:84: Tricep muscles are
(A) Flexor muscles (B) Extensor muscles
(C) Adductor muscles (D) Abductor muscles
Q:85: A muscle which moves a body part away from the mid line of the body is
(A) Flexor muscle (B) Extensor muscle
(C) Adductor muscle (D) Abductor muscle
Q:86: A muscle which moves a body part towards the mid line of the body is
(A) Flexor muscle (B) Extensor muscle
(C) Adductor muscle (D) Abductor muscle
Q:87: In earth worm contraction of ____________ muscles shortens the body.
(A) Longitudinal (B) Circular
(C) Protractor (D) Adductor
Q:88: In earth worm contraction of ____________ muscles lengthens the body.
(A) Longitudinal (B) Circular
(C) Retractor (D) Abductor
Q:89: The state of physiological inability of a muscle to contract due to accumulation of lactic acid is referred to as
(A) Rigor mortis (B) Muscle fatigue
(C) Muscle tetany (D) Muscle cramp
Q:90: The stationary part of skeletal muscle is known as
(A) Origin (B) Insertion
(C) Belly (D) Ligament
Q:91: The movement in Jelly fish is called
(A) Bell propulsion (B) Jet propulsion
(C) Float propulsion (D) None of these
Q:92: Cross bridges form between
(A) Troponin and tropomyosin (B) Calcium and sodium
(C) Sarcolemma and sarcoplasm (D) Myosin head and Actin filament
Q:93: The limb bones first appeared in
(A) Jawless fishes (B) Lobe finned fishes
(C) Amphibians (D) Reptiles
Q:94: Select the correct for diagram below
(A)"A" Myosin, "B" Actin, "C" H-zone (B) "A" Myosin, "B" Actin, "C" M-lines
(C) "A" Actin, "B" Myosin, "C" Z-lines (D) "A" Troponin, "B" Tropomycin, "C" Z-lines
(C) "A" Actin, "B" Myosin, "C" Z-lines (D) "A" Troponin, "B" Tropomycin, "C" Z-lines
Answer Key:
1. D
2. C
3. C
4. C
5. D
6. A
7. D
8. C
9. C
10. B
11. B
12. A
13. D
14. B
15. A
16. B
17. C
18. D
19. C
20. A
21. C
22. C
23. C
24. D
25. D
26. C
27. C
28. B
29. C
30. D
31. D
32. B
33. B
34. C
35. C
36. B
37. A
38. D
39. C
40. D
41. B
42. C
43. D
44. C
45. A
46. A
47. B
48. C
49. D
50. C
51. A
52. C
53. A
54. A
55. A
56. B
57. C
58. A
59. C
60. B
61. A
62. D
63. D
64. A
65. D
66. B
67. C
68. D
69. B
70. B
71. C
72. D
73. A
74. C
75. B
76. A
77. B
78. B
79. B
80. C
81. D
82. A
83. A
84. B
85. D
86. C
87. A
88. B
89. B
90. A
91. B
92. D
93. C
94. C
Chapter=2
Support and movement



sir make a new type mcqs in which ans is given .dont show a key
ReplyDeleteSir ne blkul sahi kiya hai because key lazim honi chahiye agar key e nh hogi to hum yad kese karenge baki agar apko key nh chahaiye to ap online tests dien baki hamare liye key bht achi q k pehle solve karo bad me key ko dekho .....and thanks alot sir hamari help k liye
Deleteyes its true
Deleteabsoluty write sister
Deleteagr key nhn hotii to dhuke lagane prte
thanks sir for biology mcqs its really helpful for all students . Biology mcqs
ReplyDeletecorrect the option 20 it is not nycteinastic it is photonasty.
ReplyDeleteIt's a beautiful way to learn thanks alot sir mansoor
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteGreat Website For MCAT Exams Quiz
ReplyDeletesir plz upload mcqs of all chapters of both 1st n 2nd year
ReplyDeleteSir thank for mcqs b/c it is very helpful to students for their study
ReplyDeleteSIr give new mcqs
ReplyDeleteNice
ReplyDeleteQ:57: It is spinal degeneration and deformity of the joints of two or more vertebrae that commonly occurs with aging.
ReplyDelete(A) Sciatica (B) Osteoporosis
(C) Spondylosis (D) Both B and C
Can anyone tell how spondolysis is the ans of this qUESTION
C
DeleteSpondylosis
DeleteYes
ReplyDeleteBecause osteoporosis and sciatica is Not Answer of this Question
ReplyDeleteThen Only this Option is Remains
Really have a good mcqs with key now we have easily count our score and what we have...
ReplyDeleteMovment of the railway creeper around a rope is not zigzag movement
ReplyDeleteNot nutation which is due to diffential growth.
Its tropism means turning movement such as climbing vines is also tropism.
Great effort dear Sir thank yu 💫
ReplyDeleteGreat effort Dear Sir
ReplyDeleteThank you so much.